A Handbook of E-Lit Reading
In collaboration with Erik Radio, Metadata Librarian at UC. Boulder
The changes effected by digital platforms on reading continue to be a contested area in popular culture, pedagogy, and higher education. It is also an area where electronic literature (e-lit), digital humanities scholarship, and information science can shed much light. Works of e-lit are a rich testing ground to explore how creative, non-commercial uses of digital media have been exploited and proposed to readers. In a Handbook of Electronic Literature Reading, we explore the reading instructions accompanying e-lit works to investigate the performative engagement of reading from the perspective of storage medium, objects and modes of interaction, and gestures or actions. The data included in the reading instructions shed light on how reading practices have morphed depending on platform historically over the last three decades. This focus has warranted an examination into current bibliographic practices to determine how the new modalities of e-lit require different descriptive methods and approaches to metadata creation.
Background:
To say that digital reading platforms (web, e-readers, smartphones, etc.) are changing the way reading has been practiced in the age of print is now a truism. Often, these shifts have been the object of elegiac meditations (Birkerts, Manguel) and pedagogical concerns (NEA’s “Reading at Risk” and “To Read or Not to Read”). These approaches highlight the ‘erosion’ that the practice of reading is undergoing. A useful corrective has been Andrew Piper’s Book Was There. His call to think about reading from the basis of “the relationship between reading and hands, [and] the long history of how touch has shaped reading and, by extension, our sense of ourselves while we read” (3) has brought to light the bodily handling of reading objects. Our understanding of reading and text as a performative kind of practice has begun to take shape. For Rita Raley, text is “the whole of the event, its physical, logical, and conceptual architecture; the enactment and experience; its temporal structures; and associated social and juridical protocols” (2013: 21). Similarly, for Johanna Drucker, we need to elaborate “a different conception of artifacts (books, documents, works of textual or graphic art), one in which reception is production and therefore all materiality is subject to performative engagement within varied, and specific, conditions of encounter” (2014).
Electronic Literature Instructions:
Though a sizeable body of e-lit scholarship has focused on matters like textuality, software, meaning making systems, code, preservation, etc. reading has not been at the forefront. The experimental qualities of e-lit have produced a great diversity of interaction modalities and ways of handling the objects that supports said experimentation. Nevertheless, an understudied convention of e-lit are the instructions accompanying most works. These instructions go from some of the most radically sensuous like Serge Bouchardon’s Blow, “Blow to read the text then to spread the words. This scene requires a microphone” (Fig 1); to more conventional ones like “click your mouse at the right edge of the screen to move right to a new region of texts [and] tap the arrow keys to move” from Nick Montfort and Stephanie Strickland’s Sea and Spar Between (Fig 2).
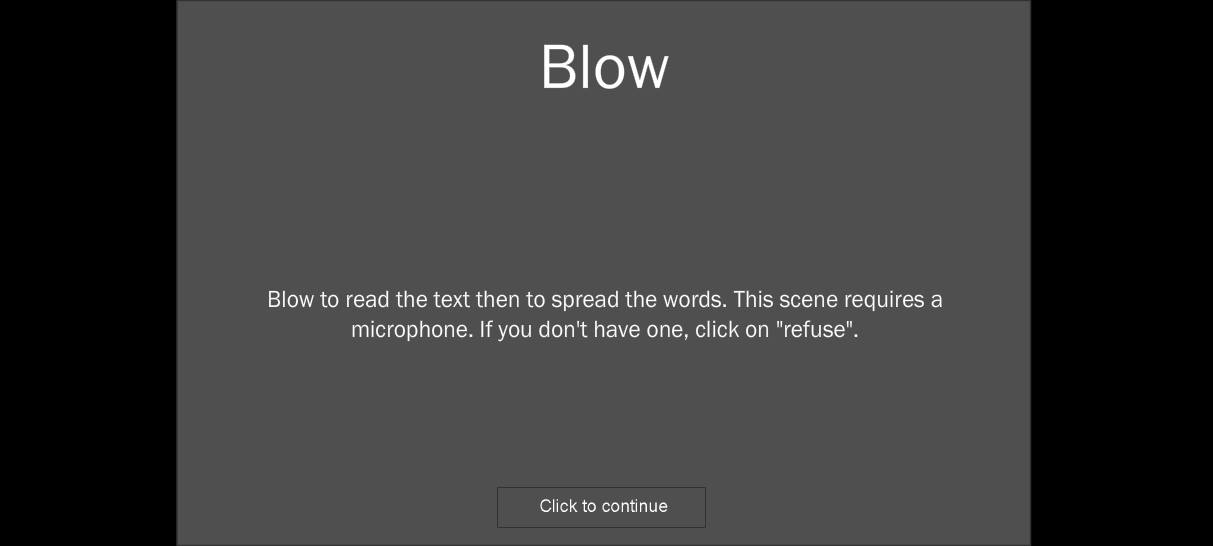
The paratextual dimension of these instructions has been on the margins of the studies focusing on particular works. Cumulatively, however, the information kept on these reading instructions can signal the shifts that e-lit has enacted on reading in digital platforms. Even more broadly, as a sample of the many experimental and still unstable standards of reading in digital platforms, e-lit reading instructions can offer evidence of practices that may be becoming more integral to the act of reading. Similarly, the mentions of the hardware (mouse, microphone, keyboard, etc.) required to read e-lit works provide detailed insights on the historical role that technological developments have enacted on reading as a performative engagement.

Metadata and Description:
The new affordances offered by e-lit increase the scope of bibliographic practices in ways that allow for more coordinated retrieval but also create greater depth and specificity in records as datasets. Many descriptive metadata standards have been largely shaped by the predominance of print media, and while its qualities overlap with those of e-lit, emerging characteristics of the latter require extensible structures to be considered comprehensively described. E-lit specific metadata sets have been developed by initiatives like Electronic Literature as a Model of Creativity and Innovation in Practice (ELMCIP) and the Electronic Literature Directory (ELD). However, among them there is still a variety of descriptive approaches and objectives. The Consortium on Electronic Literature (CELL) has taken significant steps towards interoperability and a “consensual model for the object of this field” (Baldwin) while still acknowledging the particular interest of individual archives and datasets. Efforts like this may still be enhanced through greater reconciliation with existing bibliographic procedures. In e-lit the interaction between a work and a reader poses new ontological considerations for descriptive orientations suitable to examine the particularities of reading in digital platforms. Hayles’ concept of intermediation proposes that the emergent processes that occur when reading e-lit forms a dynamic heterarchy in which both reader and work continuously inform and shape the trajectory by which reading unfolds (2007:100). This process reframes the ontic nature of work and reader, dissolving the duality into a single event. New qualities surface as a result, highlighting the different modalities through which intermediation occurs and inform bibliographic projects. Navigating these qualities and the language with which they are described poses new challenges for interoperability with similar collections in addition to being synthesized into the extensive legacies of bibliographic practices.
Proposed Metadata Elements
- Storage Medium - hardware that contains the work
- Object of Interaction - hardware mediating between reader and work
- Mode of Interaction - how the objects of interaction are physically used
- Trajectory - how a work unfolds
- Prehension Mode - how a work engages a reader into certain actions
The Handbook:
A Handbook of E-Lit Reading collects screenshots of the reading instructions of e-lit works and documents them according to storage medium (web, iPad, CD-ROM, floppy disk, etc.), actions or gestures (blow, click, scroll, type, etc.) and hardware (web cam, keyboard, mouse, microphone, etc.). The pilot target corpus includes ~200 works from over twenty countries anthologized in the Electronic Literature Collections Vol. 1, 2, and 3. The data extracted from the instruction pages will be analyzed and crossed referenced in order to observe emerging patterns like most common practices, most resilient ones, the rise and fall of some of them, as well as the introduction of new technological developments in hardware or software that have marked important shifts in the creation and reading of e-lit. This corpus, though not exhaustive, provides a starting point to design a suitable metadata set and test the categories included in it. Ultimately, the corpus will also encompass enough data to start drawing hypothesis and signal future directions for the project.